Electric Vehicles BEV
Table of Contents
I. Introduction to Electric Vehicles

A. Definition of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a revolutionary mode of transportation designed to reduce reliance on traditional fossil fuels and mitigate the environmental impact associated with internal combustion engine vehicles. These vehicles utilize electric propulsion systems, with power sourced from rechargeable batteries or a combination of batteries and an internal combustion engine.
B. Significance of Electric Vehicles in the Transportation Industry
The adoption of electric vehicles plays a pivotal role in addressing global concerns related to climate change and air pollution. As governments and industries push for sustainable practices, EVs offer a cleaner alternative to conventional vehicles, contributing to a greener and more environmentally conscious future.
C. Transition towards Sustainable Mobility
The automotive industry is undergoing a transformative shift towards sustainable mobility. Factors such as advancements in battery technology, supportive government policies, and growing consumer awareness are driving this transition. Electric vehicles, including BEVs, HEVs, and PHEVs, stand at the forefront of this revolution.
II. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) Explained
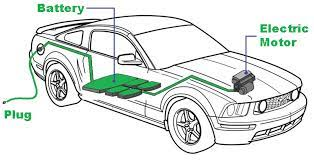
A. Definition and Characteristics of BEVs
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) represent the epitome of electric mobility, relying solely on electric batteries to power an electric motor. Unlike hybrid vehicles, BEVs lack an internal combustion engine, offering a zero-emission solution for environmentally conscious consumers.
B. Working Mechanism of BEVs
BEVs operate on the principle of storing electrical energy in high-capacity batteries. These batteries, usually lithium-ion, power an electric motor that propels the vehicle. The absence of a traditional engine simplifies the design and reduces maintenance requirements.
C. Advantages of BEVs
BEVs boast several advantages, including zero tailpipe emissions, lower operating costs, and a quieter driving experience. The continuous evolution of battery technology is extending the range of BEVs, making them a viable option for various consumer needs.
D. Challenges and Solutions in the BEV Industry
While BEVs offer numerous benefits, challenges such as limited charging infrastructure and range anxiety persist. Ongoing efforts in research and infrastructure development, coupled with increased public awareness, are gradually addressing these challenges.
E. Case Studies and Success Stories of Prominent BEV Models
Highlighting successful BEV models and their impact on the market provides valuable insights into the diverse options available to consumers. Case studies on popular models like the Tesla Model 3 or Nissan Leaf can showcase the capabilities and advancements within the BEV segment.
III. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) Decoded
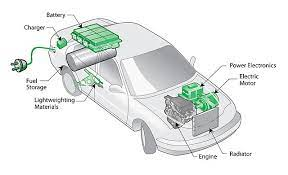
A. Introduction to Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) combine the benefits of both internal combustion engines and electric motors. They operate on an intricate system that optimizes fuel efficiency by intelligently switching between the two power sources.
B. Dual Power Source – Internal Combustion Engine and Electric Motor
HEVs utilize an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, working in tandem or independently based on driving conditions. This dual-power setup enables improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions compared to traditional vehicles.
C. Operating Modes of HEVs
HEVs typically operate in three main modes: electric-only mode at low speeds, gasoline-only mode for high-speed cruising, and a combined mode that utilizes both power sources during acceleration or when additional power is required.
D. Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Impact
One of the primary advantages of HEVs is enhanced fuel efficiency, especially in stop-and-go traffic. The reduced reliance on the internal combustion engine contributes to lower emissions, making HEVs an environmentally friendly alternative.
E. Popular HEV Models and Their Performance
Examining popular HEV models, such as the Toyota Prius or Honda Insight, provides valuable insights into the success and performance of hybrid technology. Consumer preferences and the impact of HEVs on the automotive market can be explored through these case studies.
IV. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) Explored
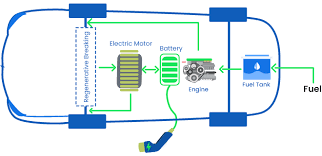
A. Definition and Characteristics of PHEVs
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) represent a hybrid evolution, offering the flexibility of electric-only driving for a limited range before seamlessly transitioning to a conventional hybrid mode. What distinguishes PHEVs is their ability to be charged externally, allowing users to tap into grid electricity for extended electric-only operation.
B. Dual Charging Capability – Electric Grid and Internal Combustion Engine
The dual charging capability of PHEVs makes them unique. Owners can charge their vehicles using external power sources, such as home or public charging stations, while retaining the convenience of an internal combustion engine for longer journeys, providing a practical solution for users with varied driving needs.
C. Advantages and Limitations of PHEVs
PHEVs combine the benefits of electric-only driving with the extended range provided by the internal combustion engine. They offer reduced emissions during electric-only operation and the convenience of using gasoline for longer distances. However, PHEVs may carry additional weight due to the dual powertrain, impacting overall efficiency.
D. Technological Advancements in PHEV Design
Ongoing advancements in PHEV technology focus on improving battery efficiency, increasing electric-only range, and optimizing the seamless transition between electric and hybrid modes. Innovations in regenerative braking systems and lightweight materials contribute to enhancing overall performance and sustainability.
E. Market Trends and Consumer Adoption of PHEVs
Analyzing market trends and consumer preferences regarding PHEVs sheds light on the growing acceptance of this hybrid variant. Factors such as government incentives, environmental awareness, and improvements in charging infrastructure play a crucial role in shaping the market dynamics of PHEVs.
V. Comparative Analysis of BEVs, HEVs, and PHEVs
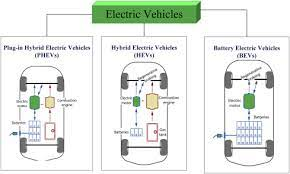
A. Performance Metrics – Range, Efficiency, and Acceleration
Comparing the performance metrics of BEVs, HEVs, and PHEVs involves assessing factors such as electric-only range, overall fuel efficiency, and acceleration capabilities. Understanding how each type excels in different scenarios allows consumers to make informed choices based on their specific needs and preferences.
B. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Examining the environmental impact of each vehicle type involves assessing factors beyond tailpipe emissions. Life cycle assessments, including manufacturing processes and energy sources for electricity generation, provide a holistic view of the sustainability of BEVs, HEVs, and PHEVs.
C. Cost Considerations – Initial Investment and Operational Expenses
Cost remains a critical factor influencing consumer decisions. Analyzing the initial investment, operational expenses, and potential savings, including fuel and maintenance costs, provides valuable insights into the overall economic feasibility of each electric vehicle type.
D. Consumer Considerations and Preferences
Understanding consumer considerations and preferences involves delving into aspects such as charging infrastructure availability, driving habits, and the desire for reduced environmental impact. Recognizing the diverse needs of consumers is essential for automakers and policymakers aiming to promote sustainable mobility.
VI. Future Prospects and Innovations in Electric Vehicles

A. Emerging Technologies in Battery and Charging Infrastructure
The future of electric vehicles holds exciting developments in battery technology. Advancements aim to enhance energy density, reduce charging times, and extend the overall lifespan of batteries. Solid-state batteries, for instance, show promise in addressing some of the limitations of current lithium-ion batteries, potentially revolutionizing the electric vehicle landscape.
B. Government Initiatives and Incentives Driving EV Adoption
Governments worldwide are recognizing the pivotal role of electric vehicles in achieving sustainability goals. As a result, various initiatives and incentives are being implemented to encourage the adoption of EVs. These include tax credits, rebates, and investments in charging infrastructure to create a conducive environment for both manufacturers and consumers.
C. Industry Collaboration and Research Developments
The electric vehicle industry is marked by collaboration and research endeavors aimed at overcoming technological challenges. Partnerships between automakers, technology companies, and research institutions foster innovation. Collaborative efforts to develop standardized charging protocols and grid integration solutions play a crucial role in advancing the electric vehicle ecosystem.
D. Predictions for the Future of Electric Vehicles
Predicting the future of electric vehicles involves considering trends in consumer behavior, technological breakthroughs, and regulatory changes. Forecasts suggest a continued rise in electric vehicle adoption, with increasing diversity in models and improved affordability. The integration of smart technologies, such as autonomous driving capabilities, further enhances the appeal of electric vehicles.
VIII. Acknowledging Challenges and Continuous Improvement

A. Overcoming Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure
While electric vehicles have made significant strides, challenges such as range anxiety and the need for a robust charging infrastructure persist. Addressing these concerns requires collaborative efforts from governments, businesses, and technology developers to expand charging networks and enhance battery technology, reassuring consumers about the practicality of electric vehicles.
B. Global Perspectives on Electric Vehicle Adoption
Adoption rates for electric vehicles vary globally due to factors such as infrastructure development, government policies, and cultural attitudes towards sustainability. Examining case studies from different regions provides insights into the varied approaches and challenges faced by diverse markets in transitioning to electric mobility.
IX. The Role of Automakers in Shaping Electric Mobility
A. Innovation in Vehicle Design and Performance
Automakers play a pivotal role in advancing electric mobility through innovation in vehicle design and performance. The integration of cutting-edge technologies, improvements in aerodynamics, and the use of sustainable materials contribute to enhancing the appeal and efficiency of electric vehicles.
B. Meeting Consumer Expectations and Preferences
Understanding and meeting consumer expectations is essential for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Automakers must continue to refine their offerings based on consumer feedback, offering a diverse range of models that cater to various lifestyle needs and preferences.
X. The Importance of Public Awareness and Education
A. Disseminating Accurate Information
Public awareness and education are crucial components of driving the adoption of electric vehicles. Disseminating accurate information about the benefits, costs, and practicalities of electric mobility can dispel myths and misconceptions, empowering consumers to make informed choices aligned with their values and needs.
B. Collaborative Efforts for Environmental Sustainability
Encouraging collaboration between governments, businesses, and environmental organizations fosters a collective approach to achieving environmental sustainability. Public-private partnerships can drive initiatives such as clean energy incentives, environmental education campaigns, and the development of green infrastructure.
XI. Navigating Regulatory Challenges and Policy Support
A. Regulatory Frameworks and Standardization
The development of clear regulatory frameworks and industry standards is essential for the continued growth of electric mobility. Governments can contribute by establishing consistent regulations, incentivizing research and development, and promoting international cooperation for standardization.
B. Policy Support for Research and Development
Policy support for research and development initiatives is crucial for advancing electric vehicle technology. Governments can incentivize innovation through grants, subsidies, and tax credits, encouraging the automotive industry to invest in sustainable practices and propel the evolution of electric vehicles.
XII. Looking Ahead: Electric Vehicles in a Sustainable Future

A. Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
The integration of electric vehicles with renewable energy sources is a key component of achieving a truly sustainable transportation ecosystem. Pairing the adoption of electric vehicles with the growth of renewable energy infrastructure contributes to a cleaner energy grid, further reducing the environmental impact of transportation.
B. Technological Convergence and Smart Mobility
The convergence of electric vehicle technology with other smart mobility solutions, such as autonomous driving and connected infrastructure, holds immense potential for shaping the future of transportation. These technological advancements can enhance safety, efficiency, and the overall user experience, propelling us toward a more connected and intelligent mobility landscape.
XIV. Empowering Communities Through Electric Mobility

A. Community-Based Initiatives
Empowering communities to embrace electric mobility involves grassroots initiatives that focus on accessibility, education, and infrastructure development. Community-based programs, such as electric vehicle sharing platforms, can foster a sense of ownership and participation, making sustainable transportation a shared responsibility.
B. Addressing Socioeconomic Disparities
As electric vehicles become more prevalent, addressing socioeconomic disparities in access to clean transportation is paramount. Governments and organizations can implement targeted programs to make electric vehicles more accessible to diverse socioeconomic groups, ensuring that the benefits of electric mobility reach communities of all backgrounds.
XV. The Evolution of Charging Infrastructure

A. Rapid Expansion of Charging Networks
The evolution of electric mobility is intrinsically linked to the expansion of charging infrastructure. Governments and private entities must collaborate to rapidly increase the number of charging stations, making electric vehicle ownership more practical and convenient for a broader audience.
B. Smart Charging Solutions
Innovations in smart charging solutions, including grid integration and dynamic pricing models, can optimize energy usage and reduce strain on the power grid. Smart charging technology enhances the efficiency of electric vehicle charging while contributing to a more resilient and adaptive energy ecosystem.
XVI. Embracing Corporate Responsibility
A. Corporate Fleets and Sustainable Practices
Corporate entities can play a significant role in advancing electric mobility by incorporating electric vehicles into their fleets. Embracing sustainable practices, such as adopting electric company cars and installing workplace charging stations, contributes to reducing corporate carbon footprints and sets a positive example for employees and customers alike.
B. Industry Collaboration for Green Supply Chains
Collaboration within industries to create green supply chains is crucial for ensuring the sustainability of electric vehicles. From responsibly sourcing materials for battery production to implementing eco-friendly manufacturing processes, the automotive industry can reduce its environmental impact throughout the entire supply chain.
XVII. Overcoming Technological Hurdles
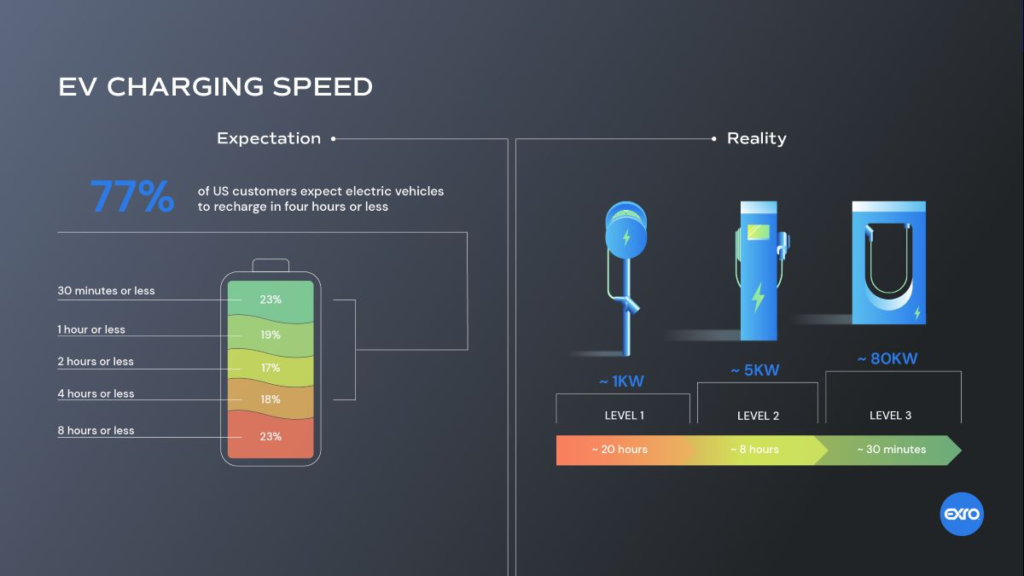
A. Research and Development for Advanced Technologies
Continued investment in research and development is essential for overcoming technological hurdles associated with electric vehicles. This includes improvements in battery technology, energy storage solutions, and lightweight materials, pushing the boundaries of innovation to enhance the efficiency and performance of electric vehicles.
B. Accessibility of Cutting-Edge Technology
Ensuring that cutting-edge technology is accessible to a broad consumer base is crucial for widespread electric vehicle adoption. Striking a balance between technological innovation and affordability is a key challenge that requires concerted efforts from both the public and private sectors.
XVIII. International Collaboration for Global Impact
A. Harmonizing Standards for Global Adoption
International collaboration is indispensable for harmonizing standards and regulations, facilitating the global adoption of electric vehicles. Standardization in areas such as charging infrastructure, safety protocols, and interoperability ensures a seamless experience for users worldwide.
B. Sharing Best Practices and Lessons Learned
Countries and regions can benefit from sharing best practices and lessons learned in the transition to electric mobility. This collaborative approach fosters a global community committed to sustainable transportation, with shared insights driving continuous improvement on a global scale.
XIX. Resilience in the Face of Challenges
A. Adapting to Market Dynamics
The electric vehicle market is dynamic and subject to various market forces. Adapting to market dynamics, consumer preferences, and unforeseen challenges requires resilience from manufacturers, policymakers, and other stakeholders. Flexibility in strategies and a proactive approach to addressing challenges are crucial for sustained growth.
B. Learning from Setbacks and Iterating Solutions
Setbacks are inherent in any transformative journey. Learning from challenges, whether they be technological, economic, or regulatory, and iterating solutions is fundamental to the resilience of the electric mobility sector. Each setback presents an opportunity for refinement and improvement.
XX. The Ongoing Evolution: A Call to Action
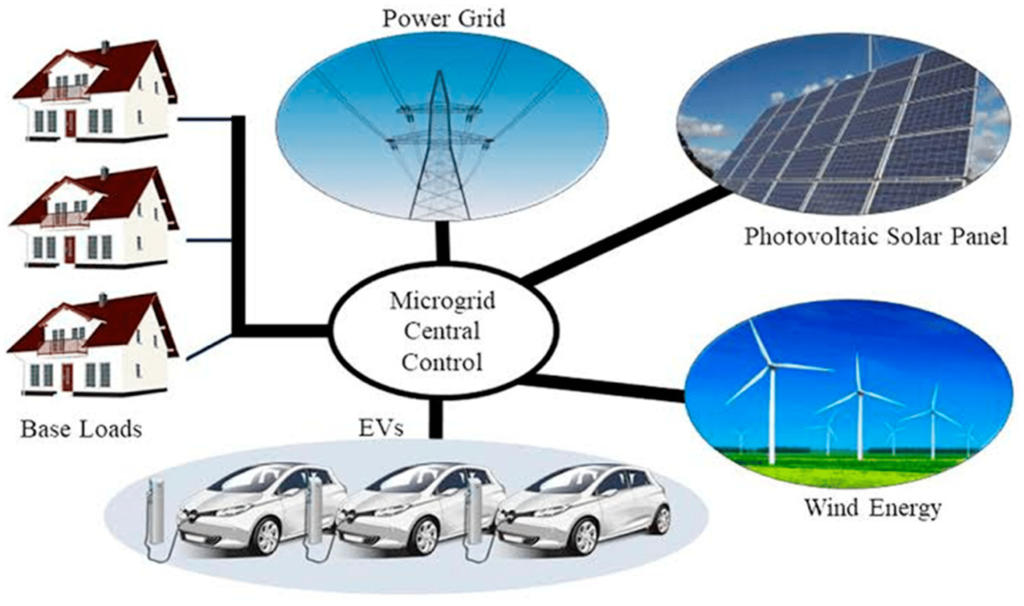
A. Empowering Individuals to Drive Change
The ongoing evolution of electric mobility is not solely the responsibility of governments and industries but requires the active participation of individuals. Empowering consumers to make sustainable choices, whether through vehicle purchases, lifestyle changes, or advocacy, is a powerful catalyst for driving positive change.
B. A Call to Action for a Sustainable Future
As we navigate the complexities and opportunities within the realm of electric mobility, there is a collective call to action. Governments, industries, communities, and individuals must join forces to accelerate the transition to a sustainable future. The electric vehicle revolution is not just about changing the way we drive; it’s about shaping a world where mobility coexists harmoniously with the health of our planet.
In conclusion, the evolution of electric vehicles is a multifaceted journey involving technological innovation, policy development, community engagement, and individual commitment. It requires a holistic and collaborative approach to overcome challenges, seize opportunities, and create a future where electric mobility is not just a mode of transportation but a cornerstone of global sustainability.
VII. Conclusion
A. Recap of Key Points
In this comprehensive exploration of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), key distinctions and advantages of each type have been highlighted. From zero-emission BEVs to the flexibility of PHEVs and the fuel efficiency of HEVs, the electric vehicle landscape offers diverse options for consumers.
B. Encouraging the Shift towards Sustainable Transportation
The transition towards sustainable transportation is an imperative for addressing environmental concerns and creating a more resilient future. Electric vehicles, in their various forms, contribute significantly to reducing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector, and their continued adoption is crucial for achieving broader sustainability goals.
C. The Role of BEVs, HEVs, and PHEVs in Shaping the Future
As technology continues to evolve and consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability, the role of Battery Electric Vehicles, Hybrid Electric Vehicles, and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles will undoubtedly expand. Each type caters to different needs, offering a range of choices for consumers with varying driving patterns and preferences.
In conclusion, the world of electric vehicles is dynamic and full of promise. Whether one opts for the all-electric experience of BEVs, the flexibility of HEVs, or the blended approach of PHEVs, the collective shift towards electric mobility represents a positive stride towards a cleaner and more sustainable transportation future. As technology continues to advance and awareness grows, electric vehicles will likely play an even more significant role in shaping the way we move from point A to B.
Search us on Google by typing Interestopedia.com

Как распознать истину?
абсолютная истина это http://www.koah.ru/kanke/62.htm/.
Pingback: 130. Damontae Kazee: Unveiling the Ultimate Defensive Dynamo - Interestopedia
vurcazkircazpatliycaz.11VwAo2ZhqSt
lubricative xyandanxvurulmus.hlb7OWcKA22j